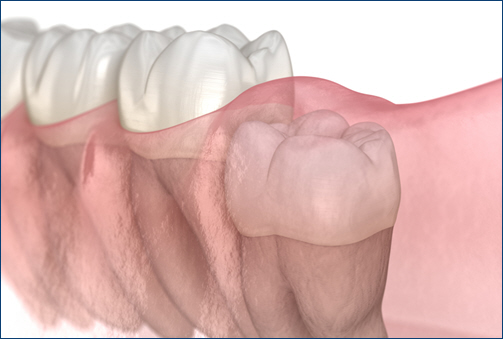
Impacted Teeth: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Impacted teeth are teeth that fail to emerge properly through the gums, often becoming stuck or misaligned. This common dental issue most frequently affects wisdom teeth, but it can also occur with other teeth, such as canines. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for impacted teeth is crucial for maintaining oral health and preventing potential complications.
Causes
-
- Lack of Space: One of the primary reasons for tooth impaction is a lack of space in the jaw. When the jaw is too small to accommodate all teeth, the new teeth may not have enough room to emerge fully, resulting in impaction.
- Abnormal Tooth Growth: Some teeth may grow at an incorrect angle, leading to impaction. This can occur due to genetics, the misalignment of other teeth, or other developmental factors that affect the natural growth of teeth.
- Overcrowding: Overcrowding in the mouth can push teeth into awkward positions, making it difficult for them to erupt properly. This is common when additional teeth grow behind existing teeth, leading to crowding and impaction.
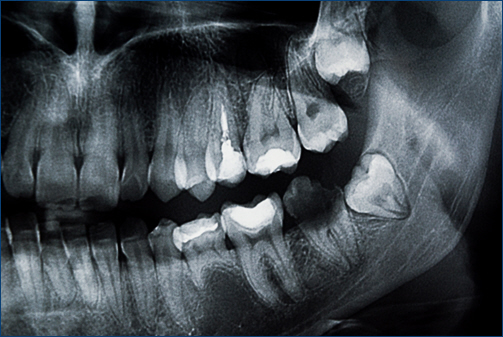 Symptoms
Symptoms
-
- Pain and Discomfort: Tooth impaction can cause significant pain and discomfort in the affected area. This pain may radiate to the jaw, ear, or neck and can worsen with chewing or biting.
- Swelling and Redness: The gums around an impacted tooth may become swollen, red, and tender to the touch. This inflammation can lead to further complications, such as infection or gum disease.
- Difficulty Opening the Mouth: In severe cases, an impacted tooth can cause difficulty opening the mouth fully, affecting eating and speaking.
- Bad Breath and Taste: The buildup of bacteria around impacted teeth can lead to persistent bad breath (halitosis) and an unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Treatment Options
-
- Monitoring and Observation: If an impacted tooth is not causing any immediate problems, a dentist may recommend regular monitoring and observation. This approach is suitable for asymptomatic impacted teeth, particularly in older patients who may not require intervention.
- Surgical Extraction: In cases where impacted teeth cause pain, infection, or damage to neighboring teeth, surgical extraction may be necessary. The procedure involves removing the impacted tooth to alleviate symptoms and prevent further complications.
- Orthodontic Treatment: For impacted canines or other teeth that need to be aligned properly, orthodontic treatment may be recommended. Braces or other appliances can help guide impacted teeth into their correct position over time.
- Pain Management and Antibiotics: To manage pain and prevent infection, dentists may prescribe pain relievers and antibiotics. These medications can help alleviate symptoms while preparing for further treatment.
Impacted teeth can cause a range of symptoms and complications if left untreated. Understanding the causes and recognizing the signs of impaction can help you seek timely dental care and explore appropriate treatment options. Whether through monitoring, surgical extraction, or orthodontic intervention, addressing impacted teeth is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing future dental issues. If you suspect you have an impacted tooth, consult your dentist for a comprehensive evaluation and personalized treatment plan.